English
English-
 English
English -
 Español
Español -
 Português
Português -
 русский
русский -
 Français
Français -
 日本語
日本語 -
 Deutsch
Deutsch -
 tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt -
 Italiano
Italiano -
 Nederlands
Nederlands -
 ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย -
 Polski
Polski -
 한국어
한국어 -
 Svenska
Svenska -
 magyar
magyar -
 Malay
Malay -
 বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার -
 Dansk
Dansk -
 Suomi
Suomi -
 हिन्दी
हिन्दी -
 Pilipino
Pilipino -
 Türkçe
Türkçe -
 Gaeilge
Gaeilge -
 العربية
العربية -
 Indonesia
Indonesia -
 Norsk
Norsk -
 تمل
تمل -
 český
český -
 ελληνικά
ελληνικά -
 український
український -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 فارسی
فارسی -
 தமிழ்
தமிழ் -
 తెలుగు
తెలుగు -
 नेपाली
नेपाली -
 Burmese
Burmese -
 български
български -
 ລາວ
ລາວ -
 Latine
Latine -
 Қазақша
Қазақша -
 Euskal
Euskal -
 Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan -
 Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk -
 Македонски
Македонски -
 Lietuvos
Lietuvos -
 Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel -
 Română
Română -
 Slovenski
Slovenski -
 मराठी
मराठी -
 Srpski језик
Srpski језик
What Are the Applications of Special Shaft High Precision Linear Shaft in Scientific Research?
2025-06-20
Special Shaft High Precision Linear Shaft is the core transmission component of precision automation equipment and scientific research instruments. Its design, manufacturing and performance far exceed those of conventional linear guides.
Excellent positioning accuracy and repeatability: This is its most core feature. It usually has micron (μm) or even sub-micron positioning accuracy and repeatability (such as ±1μm or higher). This is essential for tasks that require extremely high precision.
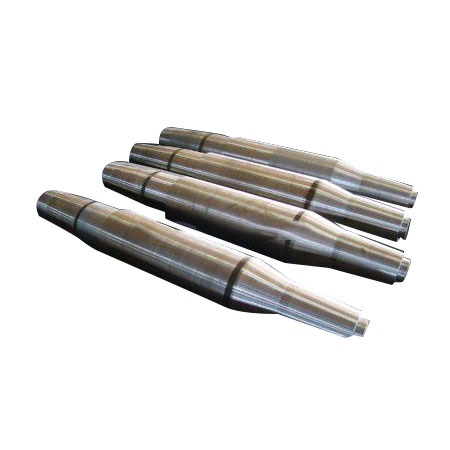

Extremely low motion error: Straightness error: The deviation of the motion trajectory from the ideal straight line is extremely small. Flatness error: The deviation of the motion plane from the ideal plane is very small.
Pitch/yaw/roll error: The rotation angle error of the axis around each axis during movement is strictly controlled. Abbe error: The design greatly reduces the influence of Abbe error by optimizing the structure (such as the colinear/coplanar design of the guide rail and the measuring point) or using compensation algorithms.
High rigidity: Special Shaft High Precision Linear Shaft has a solid structural design, and its materials and manufacturing processes are excellent, which enables it to resist small deformations caused by external loads (especially lateral forces or moments), ensuring that it can still maintain high precision under load. Friction and smooth motion: High-performance guide methods (such as preloaded ball guides, roller guides, hydrostatic guides, and air-floating guides) are used, with low and stable friction. This achieves extremely smooth uniform motion (no creep) and fast start-stop response. Excellent thermal stability and environmental adaptability: Use materials with extremely low thermal expansion coefficients (such as ceramics, special alloys), or compensate for thermal deformation through structural design/active temperature control to ensure accuracy in temperature rise or fluctuating environments. Some models have good anti-pollution capabilities (especially air floating, magnetic levitation) or vacuum compatibility.
High-resolution feedback system: Usually integrated ultra-high-resolution linear grating scales (such as nanometer resolution) or laser interferometers as closed-loop position feedback are the basis for achieving nanometer-level control.
Main application areas: Semiconductor manufacturing and inspection: Lithography machine (step-scan): The core of the wafer stage and mask stage is the nanometer-level precise positioning. Wafer inspection equipment: The precise movement of the probe station and microscopic imaging platform for defect inspection and measurement. Chip packaging and testing: The core motion axis of high-precision placement machines, wire bonding machines, and test sorting machines. Precision optics and photonics: Optical component processing and inspection: Laser direct writing, diamond turning machine tools, and positioning axes of interferometer platforms.
Microscope (confocal, super-resolution): Nanoscale scanning and positioning of the stage and objective lens. Laser processing equipment: The axis for precise positioning of the beam path or workpiece in micro-processing, marking, drilling, and cutting equipment. High-end metrology and inspection: Three-coordinate measuring machine: High-precision movement of the measuring arm in three-dimensional space.
Profilometer/roughness meter/roundness meter: Precise positioning and scanning movement of sensors.
Laser tracker/interferometer calibration platform: Provides precise reference motion path. Life science and medical equipment: Gene sequencer: Precise stepping and focusing of sample stage and optical scanning head. Cell manipulation/microinjection equipment: Precise aiming and movement of microneedles or laser beams. High-end medical imaging equipment: Precise positioning components of detectors in PET/CT/MRI. Advanced manufacturing and scientific research:
Ultra-precision machining center: Feeding movement of machine tool tool axis. FIB/SEM: Sample stage manipulation in focused ion beam/scanning electron microscope. Material science experimental platform: Precise positioning, loading or measurement of tiny samples. Quantum technology experimental device: Ultra-precision displacement control under extreme environment (low temperature, vacuum) is required. Aerospace and defense: Inertial navigation equipment test bench, optical aiming system, precision servo control mechanism, etc.
Special Shaft High Precision Linear Shaft is the basic hardware for achieving cutting-edge technological breakthroughs and production process upgrades. Its characteristics of "high precision, high rigidity, high stability and low error" make it an indispensable key core component in fields such as chip manufacturing, precision measurement, biomedicine, cutting-edge scientific research, etc. that have strict requirements on motion accuracy, and directly determine the performance upper limit of the equipment.